The world is still shaking from the recent WannaCry ransomware attack. The largest cyberattack in England’s National Health Service (NHS) history, this virus may cost innocent people their lives as medical institutions scramble to regain sanity after being infected. Find out what happened, who’s to blame, and how this can be avoided in the future.
How Cybercrooks Made the World Wanna Cry
Global institutions were paralyzed, unable to treat patients after the WannaCry attack that froze medical records, locking down all systems. The medical sector was severely hit, but it was more widespread. Germany’s railway network screeched to a halt as hackers took charge of the Deutsche Bahn computer system. Spain’s Telefonica was also hit, along with FedEx in the U.S., and many others.
The total damage was astronomical. WannaCry infected 250,000 systems, spreading itself across 99 countries around the globe.
How Did This Happen?
Such an attack left many wondering how all this was even possible. A tool called Eternal Blue is a weapon developed by the NSA to be used to retrieve information or gain access to computers of terrorists and other nefarious organizations. It gives users the ability to hack into any Windows OS computer. This tool was stolen by hacking organization Shadow Brokers, who put the virus onto an open server where other groups could utilize it for malicious intent. Computers with outdated software or ones who failed to upgrade to newer versions were susceptible to the attack.
The Far-Reaching Effects
Among the tens of thousands of institutions that were affected by the Eternal Blue malware, were many hospitals, including these British establishments:

- Barts Health Tru
- Derbyshire Community Health Services Trust
- Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust
- NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde
- NHS Fife, Western Isles, Tayside, Grampian, National Services
- Colchester General Hospital
- Scottish Ambulance Services
…among many others. In fact, roughly 20% of UK’s NHS fell.
The Damage Toll Rises
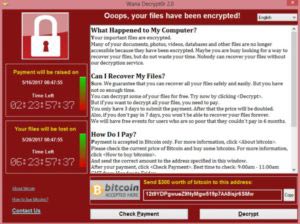
The Eternal Blue malware infected computers and effectively took control of the entire system. A warning sign showed up on the infected machine informing the user that files were inaccessible. The only way to retrieve these files was to pay the ransom, between $300 and $600. The immediate fallouts of this virus were devastating. Appointments and surgeries were cancelled because important records such as allergies, x-rays, blood tests, and medical histories were inaccessible. Ambulatory services were unable to respond to emergency calls properly, being diverted to different hospitals that hadn’t been affected.
Some hospitals were turning patients away, while others hung signs saying only truly life-threatening emergencies would be treated. Hospital staff was forced to use antiquated practices, sending patients off with hand-written prescriptions and taking notes with simple pen and paper.
The Global Response
The U.S. healthcare systems along with the U.S. Department of Homeland Security and GCHQ’s National Cyber Security Centre were quick to rally. They worked tirelessly to update older operating systems that had patches available. Additionally, Microsoft pushed an automatic update patch for all software versions. All security software was updated as well.
Meanwhile, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued an alert warning those in healthcare and public health organizations to boost their cybersecurity practices following the WannaCry attack.
Who’s Really to Blame?
Where to point the finger of blame is a heated topic. Shadow Brokers stole the virus and put it out for cybercriminals to access, but they’re not the ones who used it. So who is really to blame? On the one hand, hospitals were using outdated software that they should have upgraded long ago. With a simple click of a button, this entire mess could have been avoided, making a strong case against individuals who didn’t upgrade out of sheer laziness.

Many NHS servers were left with ancient software versions, using obsolete systems and leaving gaping holes in the security for months. One figure showed that 90% were using 16-year old software. The NHS is responsible for the entire healthcare system,
they should have been aware of and penalizing anyone with outdated software.
Finally, many are furious with the NSA. This is not the first time that a hacking group stole national security files that the NSA had been cooking up and secreting away for later, and used them against the world. Several people are accusing the NSA of housing dangerous weapons that aren’t sufficiently protected, putting the entire world in peril in a very Avengers-esque sort of way.
Protecting Yourself from Cyberattacks
There is much that could have been done to avoid such a catastrophic incident, and organizations should be eager to implement procedures (old and new) – yet it remains to be seen that the OIG will jump on board and mandate new security protocols.
Some of the most important procedures and practices health compliance officers can implement to prevent similar attacks include:
- Inform employees of basic security practices such as not downloading unknown files, clicking on strange links, and connecting unprotected devices.
- Always keep security and software updated. It can save you from immeasurable damage.
- Back up files frequently onto servers or devices unrelated to your main network.
- Finally, and most importantly, make sure you ‘think before you click!’